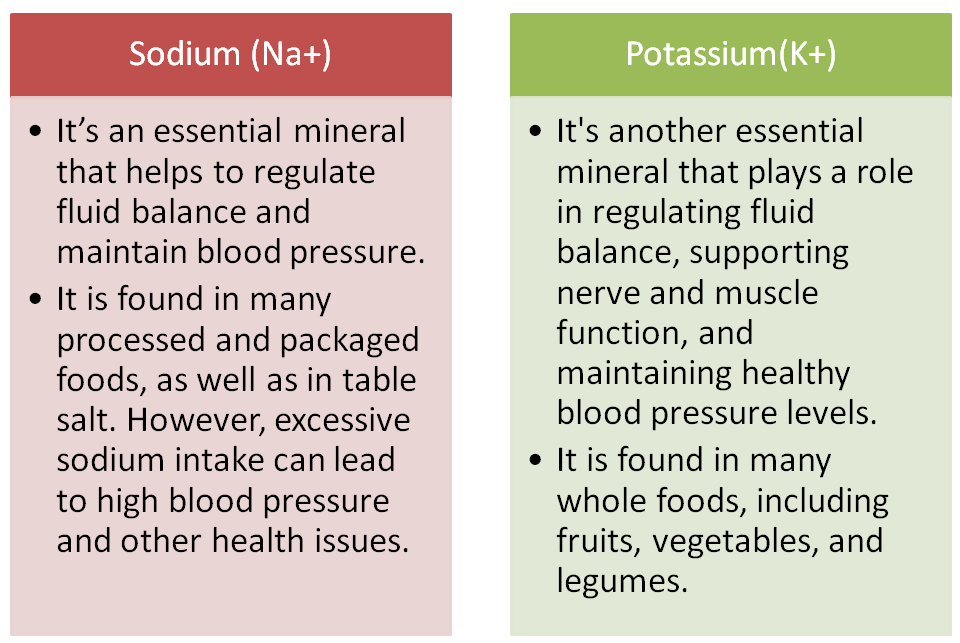
Sodium (Na) and potassium (k) are two electrolytes that play a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and supporting proper nerve and muscle function in the body. The balance between these two minerals is important for overall health.
Sodium Potassium (NaK) Imbalance Symptoms:
An imbalance in the levels of sodium and potassium in the body can have negative effects on health. Here are some potential consequences of an imbalance:
- High Blood Pressure: Sodium can cause fluid retention, which can lead to an increase in blood pressure. Potassium helps to counteract the effects of sodium and maintain healthy blood pressure levels. An imbalance of these minerals can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Increased risk of Cardiovascular Disease: High blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke. An imbalance of sodium and potassium can increase the risk of these conditions.
- Dehydration: An imbalance of sodium and potassium can affect fluid balance in the body and contribute to dehydration.
- Muscle Weakness or Cramping: Potassium is important for proper muscle function, and an imbalance of this mineral can lead to muscle weakness, cramping, or twitching.
- Fatigue or Weakness: An imbalance of sodium and potassium can affect energy metabolism and contribute to fatigue or weakness.
- Nerve and Cognitive Function: Sodium and potassium are important for proper nerve and cognitive function, and an imbalance of these minerals can affect these processes.
How it Works ?
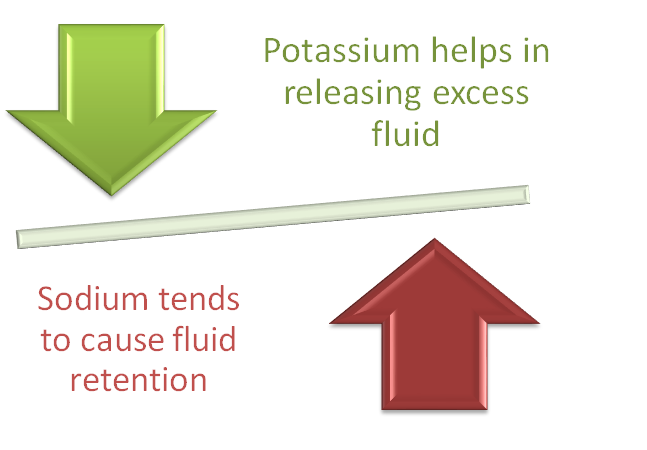
In the body, sodium and potassium work together to maintain the proper balance of fluids and electrolytes. Sodium tends to cause fluid retention, while potassium helps to release excess fluid and maintain a healthy balance. The kidneys play a key role in regulating the levels of these minerals in the body by filtering them out of the blood and excreting them in the urine.
Daily Body Requirements:
- Sodium: The recommended daily intake of sodium is less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) per day for most adults. However, some health experts recommend a lower intake, such as less than 1,500 mg per day, particularly for those who have high blood pressure or are at risk for developing it.
- Potassium: The recommended daily intake of potassium is 2,500 to 3,000 mg per day for most adults. However, some health experts recommend higher intakes, such as 4,700 mg per day, particularly for those who are physically active or have certain health conditions.
How To Maintain Sodium Potassium Balance?
Maintaining a balance of sodium (Na) and potassium (K) in your body is important for various physiological processes such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and fluid balance. Here are some ways to maintain a healthy Na K balance:
- Consume a Balanced diet: Eating a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help you maintain a healthy Na K balance. These foods are typically low in sodium and high in potassium.
- Limit Sodium Intake: Excessive intake of sodium can increase blood pressure and disrupt the Na K balance in your body. To limit your sodium intake, try to avoid processed and packaged foods, canned foods, and fast food.
- Increase Potassium Intake: Eating foods that are rich in potassium can help you maintain a healthy Na K balance. Foods such as bananas, oranges, avocados, spinach, sweet potatoes, and white beans are good sources of potassium.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration can help maintain a healthy Na K balance. Make sure to drink enough water throughout the day, especially if you are exercising or sweating heavily.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy Na K balance by improving blood circulation and reducing the risk of high blood pressure.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can increase the levels of cortisol in your body, which can disrupt the Na K balance. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help maintain a healthy Na K balance.
Summary:
It’s important to maintain a balance between sodium and potassium intake to support optimal health. A diet that is high in processed and packaged foods and low in whole foods can contribute to an imbalance of these minerals. To support a healthy sodium-potassium balance, it’s important to eat a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and to limit processed and packaged foods.
Related Posts:
Potassium Deficiency Can be Fatal ? Mind it
Factors Responsible for Cardiovascular Diseases, Check this out