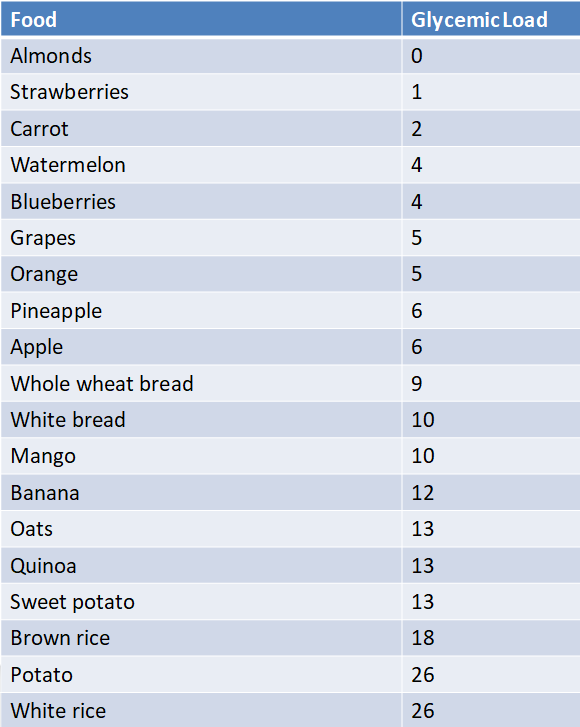
The glycemic load (GL) of a food is a measure of how much a particular food will raise blood sugar levels. It takes into account both the glycemic index (GI) of the food and the amount of carbohydrate in a typical serving size. The glycemic load is a useful parameter for understanding how different carbohydrate-containing foods may affect blood sugar levels. However, it is not the only parameter to consider when assessing the overall healthfulness of a diet.
Measures for Healthy Food
Some other parameters that may be helpful to consider include:
- Nutrient density: This refers to the amount of essential nutrients (such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber) that a food provides relative to its calorie content. Foods that are high in nutrient density can help provide the body with the nutrients it needs to function optimally.
- Antioxidant content: Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Foods that are high in antioxidants (such as fruits and vegetables) can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
- Fiber content: Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body. It helps promote satiety, regulate blood sugar levels, and support digestive health.
- Glycemic index (GI): The GI is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a lower GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
- Overall dietary pattern: Rather than focusing on individual parameters, it can be helpful to consider the overall dietary pattern. A diet that is rich in whole, minimally processed foods (such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats) is generally considered to be a healthful dietary pattern.
It’s important to note that no single parameter can provide a complete picture of the healthfulness of a diet. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods and is tailored to meet individual needs and preferences is key for optimal health.
How Glycemic Load is Calculated ?
Glycemic Load = (Glycemic Index x Grams of Carbohydrate per serving) / 100
Glycemic load of a food can be calculated as given in steps:
- Determine the glycemic index (GI) of the food you want to calculate the glycemic load for. The GI is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels on a scale of 0 to 100.
- Determine the serving size of the food in grams.
- Determine the amount of carbohydrate in the serving size of the food in grams. You can find this information on the nutrition label or in a food database.
- Multiply the GI by the number of grams of carbohydrate in the serving size, then divide by 100.
For example, To calculate the glycemic load of a medium-sized apple (GI = 38, 1 medium apple = 182 grams, 1 medium apple contains 25 grams of carbohydrate), Then Glycemic Load = (38 x 25) / 100 = 9.5 Ans: Glycemic load of a medium-sized apple is 9.5.
A food with a glycemic load of 10 or below is considered low, while a glycemic load of 20 or above is considered high.